The band YACHT, named for a mysterious sign seen in Portland around the turn of the century.
YACHT / Google I/O 2019
YACHT’s Claire Evans takes the stage not to rock out, but to talk out the band’s new album leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Google I/O 2019
The dance punk band YACHT has always felt like a somewhat techy act since debuting in the early 2000s. They famously recorded instrumental versions of two earlier albums and made them available for artists under a Creative Commons license at the Free Music Archive. Post-Snowden, they wrote a song called “Party at the NSA” and donated proceeds to the EFF. One album cover of theirs could only be accessed via fax initially (sent through a Web app YACHT developed to ID the nearest fax to groups of fans; OfficeMax must’ve loved it). Singer Claire L. Evans literally wrote the book (Broad Band) on female pioneers of the Internet.
So when Evans showed up at Google I/O this summer, we knew she wasn’t merely making a marketing appearance ala Drake or The Foo Fighters. In a talk titled “Music and Machine Learning,” Evans instead walked a room full of developers through a pretty cool open secret that awaited music fans until this weekend: YACHT had been spending the last three years writing a new album called Chain Tripping (out yesterday, August 30). And the process took a minute because the band wanted to do it with what Evans called “a machine-learning generated composition process.”
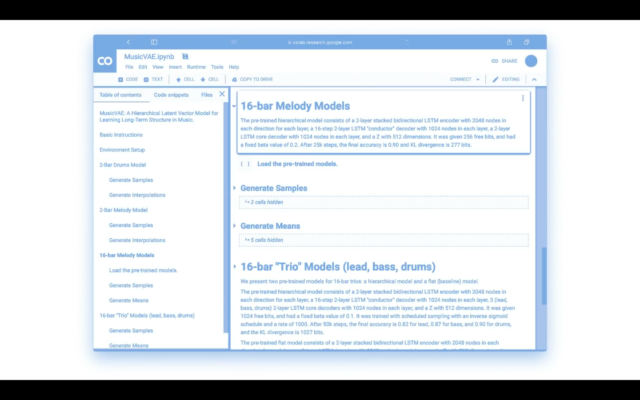
“I know this isn’t the technical way to explain it, but this allowed us to find melodies hidden in between songs from our back catalog,” she said during her I/O talk. “Here’s what the user-facing side of the model looked like when we recorded the album last May—it’s a Colab Notebook, not the kind of thing musicians usually bring into the studio.”
Enlarge / A look at YACHT’s work with MusicVAE Colab Notebook.
YACHT / Google I/O 2019
YACHT had long possessed an interest in AI and its potential application in music. But the band tells Ars it wasn’t until recently, around 2016, that the concept of doing a full album using this approach seemed feasible. While research entities had long been experimenting with AI or machine learning and allowing computers to autonomously generate music, the results felt more science project than albums suitable for DFA Records (home to labelmates like Hot Chip or LCD Soundsystem). Ultimately, a slow trickle of simplified apps leveraging AI—face swap apps felt huge around then; Snapchat and its dynamic filters rose to prominence—finally gave the band the idea that now could be the time.
“We may be a very techy band, but none of us are coders,” Evans tells Ars. “We tend to approach stuff from the outside looking in and try to figure out how to manipulate and bend tools to our strange specific purposes. AI seemed like an almost impossible thing, it was so much more advanced than anything we had dealt with… And we wanted to use this to not just technically achieve the goal of making music—so we can say, ‘Hey an AI wrote this pop song’—rather we wanted to use this tech to make YACHT music, to make music we identify with and we feel comes from us.”
Bringing a Colab Notebook to a rock studio
Having the idea to use artificial intelligence to somehow make music was one thing; doing it proved to be something else entirely. The band started by looking at everything available: “We messed around with everything that was publicly available, some tools that were only privately available—we cold emailed every single person or entity or company working with AI and creativity,” as YACHT founder Jona Bechtolt puts it. But no single existing solution quite offered the combination of quality and ease of use the band had hoped for. So, they decided to ultimately build out their own system by borrowing bits and pieces from all over, leveraging their entire back catalog in the process.
“We knew we’d have to base everything on some kind of dataset, so early on, we thought, ‘What if we used our back catalog?” Bechtolt says. “We naively thought it’d be something like Shazam, where we could throw raw audio at an algorithm. That isn’t really possible…”
“Or, at least, not within the realm of our computing capacity,” Evans interjects.
“So we had to notate all our songs in MIDI, which is a laborious process,” Bechtolt continues. “We have 82 songs in our back catalog, which is still not really enough to train a full model, but it was enough to work with the tools we had.”
With that MIDI data, Bechtolt and longtime collaborator (bass and keyboards player) Rob Kieswetter started by identifying small segments—a particular guitar riff, a vocal melody, a drum pattern, anywhere from two bars to 16 bars—that could be looped, combined, and ultimately run through the band’s simplified AI and ML model. The band relied heavily on Colab Notebooks in a Web browser—specifically, the MusicVAE model from Google’s Magenta team—manually inputting the data and then waiting (and waiting) for a fragment of output from this workflow. And that AI/ML-generated fragment, of course, was nothing more than data, more MIDI information. Evans told I/O the band ran pairs of those loops through the Colab Notebook at different temps “dozens, if not hundreds of times to generate this massive body of melodic information” as source material for new songs. From there, it became the humans’ turn.
“It still couldn’t make a song just by pushing a button; it was not at all an easy or fun flow to work through,” Bechtolt says. “So after three days, we were like, ‘OK, I think we have enough stuff.’ By that point we had a few thousand clips between two- and 16-bars, and we just had to call it quits at some point.”
“It wasn’t something where we fed something into a model, hit print, and had songs,” Evans adds. “We’d have to be involved. There’d have to be a human involved at every step of the process to ultimately make music… The larger structure, lyrics, the relationship between lyrics and structure—all of these other things are beyond the technology’s capacity, which is good.”
Listing image by YACHT / Google I/O 2019






